 (Settings/Registration).
(Settings/Registration).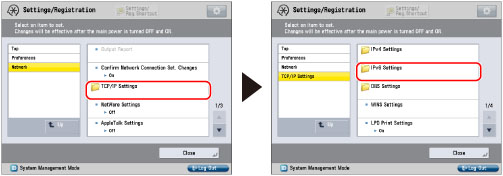
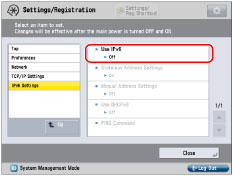
|
NOTE
|
|
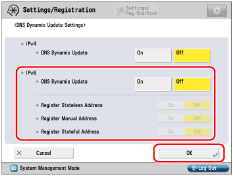
The stateless address is discarded when the machine is restarted (with the machine's main power switch ON).
|
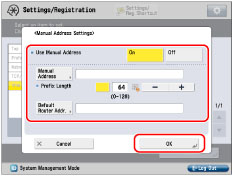
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
You cannot use a manual address if you leave [Manual Address] blank. Also, you cannot set any of the following types of address for [Manual Address]:
Multicast address
Address composed entirely of zeros
IPv4 compatible address (an IPv6 address with the top 96 bits set to '0' and an IPv4 address in the lower 32 bits)
IPv4 mapped address (an IPv6 address with the top 96 bits set to '0:0:0:0:0:ffff:' and an IPv4 address in the lower 32 bits)
You cannot enter a multicast address or an address composed entirely of zeros in [Default Router Addr.].
|
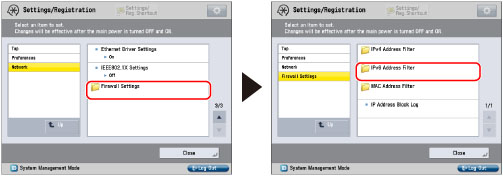
 |
 |
|
[Outbound Filter]
|
[Inbound Filter]
|
|
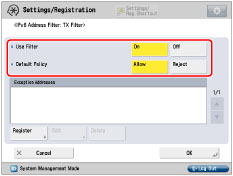
<Use Filter>
|
<Default Policy>
|
Settings Required after Pressing [Register]
|
|
|
Allow data transmission with all computers, but not with specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Allow]
|
Register IPv6 address or IPv6 address prefix you want to reject.
|
|
Reject data transmission with all computers, but not with specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Reject]
|
Register IPv6 address or IPv6 address prefix you want to allow.
|
|
Allow data reception from all computers, but not from specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Allow]
|
Register IPv6 address or IPv6 address prefix you want to reject.
Register port number for functions you want to reject.
|
|
Reject data reception from all computers, but not from specified computers.
|
[On]
|
[Reject]
|
Register IPv6 address or IPv6 address prefix you want to allow.
Register port number for functions you want to allow.
|
|
Allow data transmission/reception with all computers.
|
[Off]
|
-
|
-
|
|
NOTE
|
|
If data transmission/reception is attempted between the device, which has the IPv6 address/port number set to be rejected, and the machine, a block log will be generated. To display the block log, see "Checking the Block Log."
Information for the rejected port number is recorded in the block log only when using TCP/UDP. Port number is not recorded when using protocols which have no port number such as ICMP.
|
 |
 |
|
[Outbound Filter]
|
[Inbound Filter]
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
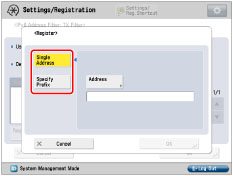
You cannot specify a multicast address for an IPv6 address.
If the usage of a protocol or print application is not permitted on your device, it cannot be used even after settings in [Firewall Settings] have been changed on your device. Configure the settings to permit the protocol or print application.
If you enter '255' in [Prefix Length], no IPv6 addresses will be set.
If you enter '0' in [Prefix Length], all IPv6 addresses will be set.
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
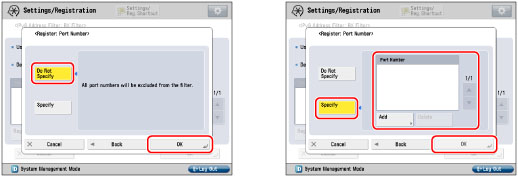
You can register up to 16 port numbers for IPv6 addresses or IPv6 address prefixes.
You can register 50 port numbers for one port number setting.
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
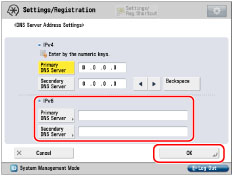
You cannot set any of the following types of address for [Primary DNS Server] or [Secondary DNS Server]:
Multicast address
Address composed entirely of zeros
Link local address
If you set <Use DHCPv6> to 'On' in step 7, the IPv6 address of a DNS server you set manually will be overwritten.
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
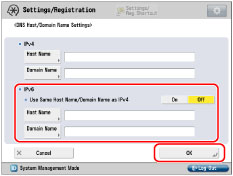
If you set <Use DHCPv6> to 'On' in step 7, the domain name you set manually will be overwritten. Even if you set <Use Same Host Name/Domain Name as IPv4> to 'On', the domain name obtained from the DHCPv6 server is used.
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
Windows Server 2003 does not support DHCPv6 servers.
If you have a DHCPv6 server running Windows Server 2008 that uses the DHCPv6 service and want to register the machine's DNS record, configure the following settings in the DHCPv6 server:
In the DHCPv6 server, right-click the [Scope] icon → click [Properties]. In the [DNS] sheet of the displayed dialog box, select [Enable DNS dynamic updates according to the settings below] → [Dynamically update DNS A and PTR records only if requested by the DHCP clients].
In the Active Directory environment, right-click the icon of the DHCPv6 server you are using → select [Properties]. In the [Advanced] sheet of the displayed dialog box, click [Credentials]. In the [DNS dynamic update credentials] dialog box, enter the user name, domain, and password for the Active Directory.
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If the IPv6 address assigned to the machine is the same as another node, you may not be able to perform IPv6 communication, even though an IPv6 address is displayed on the screen.
|