|
NOTE
|
|
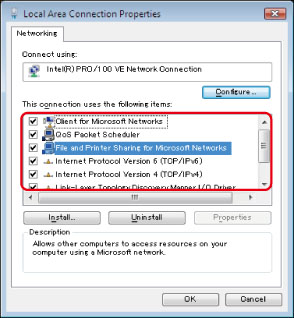
In the Active Directory environment, the procedures for setting up users differ from the above. For more information, see the Windows manual.
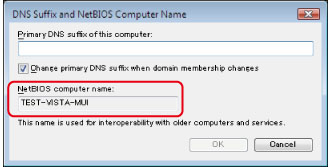
When a computer that one or more users log on to is restricted by the administrator in an Active Directory environment, the name of the computer must be registered in the Active Directory. Set the computer name in the user account properties dialog box to "CANON + the last 8 digits of the MAC address of the computer + 00". For example, if the MAC address of the computer you are using is "00:00:11:22:33:44", set "CANON1122334400".
|
|
NOTE
|
|
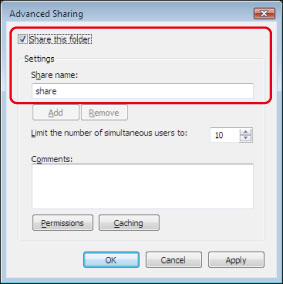
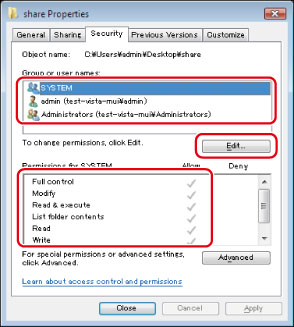
To display the [Security] tab in Windows XP, open Folder Options → deselect [Use simple file sharing]. However, you can share folders and files with [Use simple file sharing] selected. Select or deselect [Use simple file sharing] to suit your environment. For more information, see the manual provided with Windows XP.
In the Active Directory environment, the procedures for specifying the security settings of the shared folder differ from above. For more information, see the Windows manual.
|
|
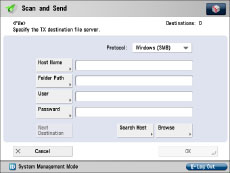
[Computer Name]/[NetBIOS computer name]:
|
swan
|
|
[Share name]:
|
share
|
|
<Protocol:>:
|
Windows (SMB)
|
|
[Host Name]:
|
\\swan\share (Shared folder path)
|
|
[Folder Path]:
|
\Images
|
|
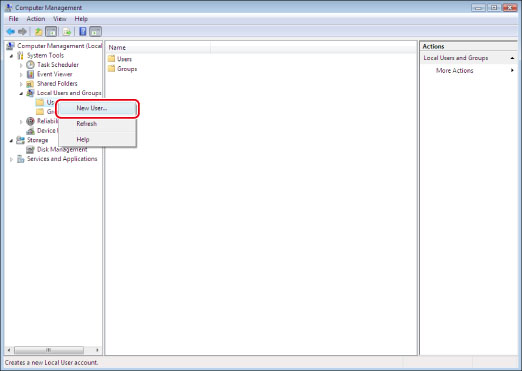
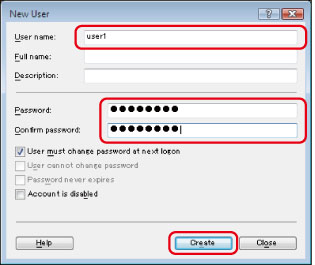
[User Name]:
|
User name entered in the above step
|
|
[Password]:
|
Password for the above user
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you want to specify each item from the list on the Browse screen, make sure you press [Browse] after the expiration of the time specified in "Startup Time Settings."
Up to 128 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Host Name] on the control panel. Also, up to 255 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Folder Path]. Specify the server settings within the character limit.
If you change the language of the touch panel display, [Host Name] and [Folder Path] may not appear correctly, or you may not be able to browse the directories.
If the language of the touch panel display differs from the computer used as a master browser, [Host Name] and [Folder Path] may not appear correctly, or you may not be able to browse the directories.
|
|
NOTE
|
|
You can send data using the following formats. A DNS server is required for the latter case:
\\192.168.2.100\share \\host_name.organization.company.co.jp\share You can send data using the following formats.
domain_name\user_name (up to 15 alphanumeric characters for the domain name, and up to 20 for the user name)
If you specify the user name in this format, the user authority for the specified domain is applied to SMB communication. user_name@organization.company.com (up to 128 characters in total)
Note that the latter is only applicable when sending to a Windows XP/Server 2003/Server 2008/Vista/7/Server 2008 R2 computer that belongs to a domain containing Windows XP/Server 2003/Server 2008/Vista/7/Server 2008 R2 domain controllers. |
|
Computer name:
|
swan
|
|
Share name:
|
share
|
|
<Protocol:>:
|
Windows (SMB)
|
|
[Host Name]:
|
\\swan\share (Shared folder path)
|
|
[Folder Path]:
|
\Images
|
|
[User Name]:
|
User name entered in the above step
|
|
[Password]:
|
Password for the above user
|
|
IMPORTANT
|
|
If you want to specify each item from the list on the Browse screen, make sure you press [Browse] after the expiration of the time specified in "Startup Time Settings."
Up to 128 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Host Name] on the control panel. Also, up to 255 alphanumeric characters can be entered for [Folder Path]. Specify the server settings within the character limit.
If you change the language of the touch panel display, [Host Name] and [Folder Path] may not appear correctly, or you may not be able to browse the directories.
If the language of the touch panel display differs from the computer used as a master browser, [Host Name] and [Folder Path] may not appear correctly, or you may not be able to browse the directories.
|
|
NOTE
|
|
You can send data using the following formats. A DNS server is required for the latter case:
\\192.168.2.100\share \\host_name.organization.company.co.jp\share You can send data using the following formats.
domain_name\user_name (up to 15 alphanumeric characters for the domain name, and up to 20 for the user name)
If you specify the user name in this format, the user authority for the specified domain is applied to SMB communication. |
|
NOTE
|
|
If you are using Windows Vista, a dialog box may appear while you are performing the procedure. In this case, enter a user name and password. For more information, see the manuals provided with the operating system.
|